If you’re considering upgrading your home’s water heating system, you’ve probably come across the increasingly popular tankless water heater. Unlike traditional water heaters that store and continuously heat water in a tank, tankless systems heat water on demand, offering greater efficiency and a seemingly endless supply of hot water. But how does a tankless water heater work, and what makes it a worthwhile choice?
1. How Does a Tankless Water Heater Work?
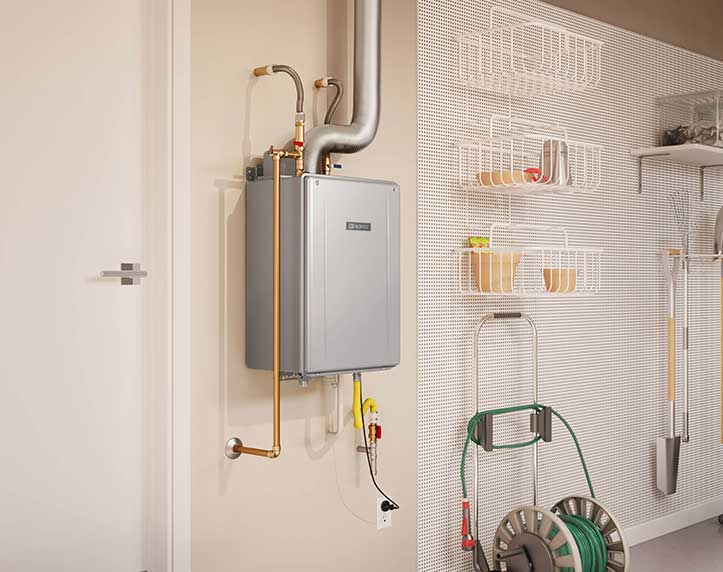
A tankless water heater operates fundamentally differently from traditional tank-style heaters. Instead of storing a large volume of heated water, a tankless water heater heats water instantaneously as it flows through the unit. Let’s break down the process step-by-step
1.1 On-Demand Heating Process
- Activation: When you turn on a hot water tap, shower, or appliance, cold water enters the tankless unit through an inlet pipe.
- Flow Sensor: A sensor detects the flow of water and activates the heating mechanism (either a gas burner or electric heating elements).
- Heating the Water: The water travels through a heat exchanger, which rapidly heats the water to the desired temperature.
- Delivery: The heated water exits the unit and flows to the faucet or appliance.
- Deactivation: When the tap is turned off, the flow sensor shuts down the heating mechanism, saving energy by stopping heat production.
1.2 Key Components of a Tankless Water Heater
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the burner or heating elements to the water.
- Flow Sensor: Detects water flow and signals the unit to start heating.
- Gas Burner or Electric Heating Elements: Provide the heat needed to warm the water.
- Control Panel: Allows you to set and monitor the water temperature.
- Ventilation System for Gas Models Safely vents combustion gases outside the home.
1.3 Types of Tankless Water Heaters
Tankless water heaters come in two main types
- Gas Tankless Water Heaters
- Use natural gas or propane.
- Heat water quickly with a powerful gas burner.
- Require proper ventilation for exhaust gases.
- Electric Tankless Water Heaters
- Use electric heating elements.
- Ideal for smaller households or point-of-use applications.
- Generally less powerful than gas models.
2. Advantages of Tankless Water Heaters
Tankless water heaters offer several benefits that make them a popular choice among homeowners
2.1 Endless Hot Water Supply
Because tankless units heat water on demand, you never run out of hot water. This makes them ideal for large families, homes with multiple bathrooms, or situations where hot water is used continuously (e.g., back-to-back showers).
2.2 Energy Efficiency
Tankless water heaters are more energy-efficient than traditional models because they don’t continuously heat a tank of water. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, tankless heaters can be 24% to 34% more efficient for homes that use 41 gallons or less of hot water daily. For higher water usage, they are still 8% to 14% more efficient.
2.3 Space-Saving Design
Tankless water heaters are compact and wall-mounted, freeing up valuable floor space. This makes them ideal for smaller homes, apartments, or places where space is at a premium.
2.4 Longer Lifespan
A well-maintained tankless water heater can last up to 20 years or more, compared to 10-15 years for traditional tank heaters. This longevity can justify the higher initial cost.
2.5 Reduced Risk of Leaks and Water Damage
Since tankless water heaters don’t store large volumes of water, there’s a lower risk of catastrophic leaks and water damage caused by tank failures.
2.6 Lower Long-Term Costs
Although the upfront installation cost is higher, the energy savings over time can help offset the initial investment. Additionally, the longer lifespan means fewer replacements.
3. Disadvantages of Tankless Water Heaters
Despite their many advantages, tankless water heaters have some drawbacks that are worth considering
3.1 High Upfront Costs
- Unit Cost: Tankless water heaters can cost between $1,000 to $3,000, depending on the model and features.
- Installation Cost: Installation can range from $2,000 to $5,000 due to the need for electrical upgrades, gas line modifications, and ventilation work.
3.2 Limited Flow Rate
Tankless heaters have a limited flow rate, typically ranging from 2 to 5 gallons per minute GPM. If multiple appliances are running simultaneously (e.g., shower, dishwasher, and washing machine), the unit may struggle to meet demand.
3.3 Requires Upgrades
- Electrical Upgrades: Electric models may require a panel upgrade to handle the higher wattage.
- Gas Line and Ventilation: Gas models often need larger gas lines and proper venting systems.
3.4 Inconsistent Temperature with Low Flow
In some cases, low water flow (like hand washing) may not activate the heating mechanism, leading to inconsistent water temperatures.
4. Tankless Water Heater Installation Process
Installing a tankless water heater is more complex than installing a traditional tank unit. Here’s a breakdown of the process
Step 1: Assessing Home Requirements
A professional plumber or contractor will
- Evaluate your home’s hot water needs.
- Check your current electrical or gas system.
- Determine the right size and type of tankless unit.
Step 2: Selecting the Right Model
Choose a unit based on
- Fuel Type: Gas or electric.
- Flow Rate: Measured in gallons per minute (GPM).
- Temperature Rise: The difference between incoming cold water and desired hot water temperature.
Step 3: Preparing the Installation Site
- Remove the Old Unit: Safely disconnect and remove the existing water heater.
- Install Mounting Bracket: Tankless units are wall-mounted, so secure the bracket in the appropriate location.
Step 4: System Upgrades
- Gas Line Upgrade: For gas models, a larger gas line may be necessary.
- Electrical Upgrade: For electric models, upgrade wiring and the breaker panel if needed.
- Ventilation: Install direct venting to expel combustion gases safely.
Step 5: Connecting Water Lines
Attach cold and hot water lines to the unit, ensuring all connections are secure.
Step 6: Testing the System
- Turn on the water supply.
- Power the unit and test for proper function.
- Check for leaks and adjust the temperature settings.
5. Is a Tankless Water Heater Right for You?
To determine if a tankless water heater is the best choice, consider the following factors
- Hot Water Usage
- Ideal for homes with moderate to high hot water demand.
- Budget
- While expensive upfront, tankless units can provide long-term savings.
- Home Size
- Great for smaller homes or homes with limited space.
- Energy Efficiency Goals
- Tankless units are excellent for reducing energy consumption.
Conclusion
Understanding how a tankless water heater works and the benefits it offers can help you decide if this upgrade is right for your home. Tankless water heaters provide energy efficiency, endless hot water, and space savings, but they come with higher installation costs and some limitations on flow rate.
If you value long-term efficiency, reduced energy bills, and a modern solution to your hot water needs, investing in a tankless water heater can be a smart choice. With proper installation and maintenance, you’ll enjoy reliable hot water for years to come.