Detecting leaks in plumbing, gas lines, or industrial systems can be challenging, especially when leaks are hidden or too small to be found by conventional methods. In these cases, ultrasound technology provides a cutting-edge solution for detecting leaks quickly, accurately, and non-invasively. But how is ultrasound used in leak detection, and why is it one of the most precise leak detection methods available?
1. What Is Ultrasound Leak Detection?
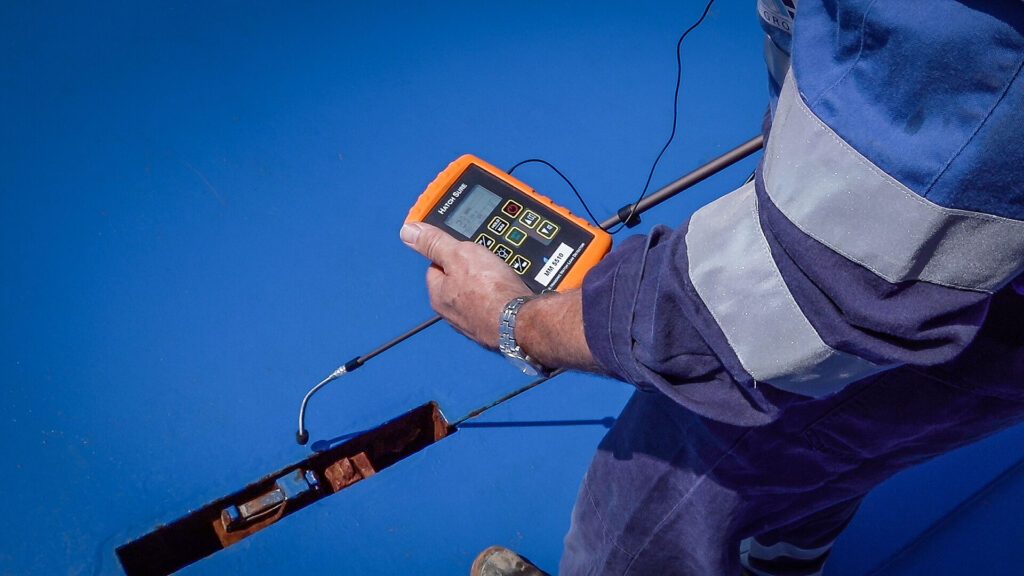
Ultrasound leak detection is a method that uses high-frequency sound waves to identify leaks in pressurized systems, plumbing, gas lines, and even compressed air systems. Ultrasounds are sounds above the range of human hearing (typically higher than 20 kHz). When gases or liquids escape from a system under pressure, they create turbulence, which generates ultrasonic noise.
Leak detection devices equipped with ultrasonic sensors can capture these high-frequency sounds, convert them into audible signals, and pinpoint the location of the leak. This method is incredibly effective because ultrasonic noise is unique and distinguishable from other environmental sounds, making it easier to isolate the source of a leak.
2. How Does Ultrasound Leak Detection Work?
Ultrasound leak detection works by capturing and analyzing the ultrasonic sounds produced by leaks. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process
2.1 Generation of Ultrasonic Noise
When a gas or liquid escapes through a crack, hole, or faulty connection in a pressurized system, it creates turbulent flow. This turbulence produces ultrasonic sound waves, which are not detectable by the human ear.
2.2 Detection with Ultrasonic Sensors
Technicians use specialized ultrasonic detectors equipped with highly sensitive microphones or sensors that can capture these high-frequency sounds. These detectors typically have
- Directional Microphones: Help isolate the source of the leak by focusing on specific areas.
- Headphones: Allow technicians to hear the converted sounds and identify leak locations.
- Visual Displays: Show the intensity and location of the ultrasonic signal on a screen for precise identification.
2.3 Signal Conversion
The ultrasonic detector converts the high-frequency sounds into a range audible to the human ear (usually between 2 to 4 kHz). This allows technicians to hear the leak in real-time, often sounding like a hissing, rushing, or popping noise.
2.4 Pinpointing the Leak
By moving the sensor across different areas, technicians can determine the exact location of the leak based on the sound’s intensity. The closer the sensor is to the leak, the louder and clearer the sound becomes.
2.5 Data Interpretation
Many modern ultrasound detectors include visual displays or digital readouts that provide data on the leak’s size, location, and severity. This information helps technicians assess the problem and recommend appropriate repairs.
3. Types of Leaks Detected by Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound leak detection is versatile and effective for identifying a wide range of leaks, including
3.1 Gas Leaks
- Compressed Air Systems: Detects leaks in air compressors, pneumatic tools, and airline systems.
- Natural Gas or Propane Lines: Identifies leaks in gas pipes and connections, preventing hazardous situations.
- Refrigerant Lines: Finds leaks in HVAC systems that could lead to reduced efficiency or environmental harm.
3.2 Liquid Leaks
- Water Pipes: Locates hidden leaks in residential or commercial plumbing systems.
- Oil and Hydraulic Systems: Identifies leaks in industrial equipment where precision and safety are critical.
3.3 Vacuum Leaks
- Industrial Vacuum Systems: Detects leaks that can compromise performance and energy efficiency.
- HVAC Systems: Finds leaks in vacuum lines that affect heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
4. Advantages of Ultrasound Leak Detection
Ultrasound technology offers several key benefits over traditional leak detection methods. Here’s why it is a preferred choice for many applications
4.1 Non-Invasive and Non-Destructive
Ultrasound leak detection does not require drilling holes, breaking walls, or disrupting operations. Technicians can identify leaks without damaging structures or systems.
4.2 High Precision
Ultrasound detectors can pinpoint leaks with remarkable accuracy, even in noisy environments. The directional microphones and visual displays help isolate the exact source of the leak.
4.3 Detects Small and Hard-to-Find Leaks
Ultrasound technology is sensitive enough to identify even the tiniest leaks that might go unnoticed by other methods. This is crucial for preventing small leaks from becoming major problems.
4.4 Fast and Efficient
Ultrasound detection provides real-time results, allowing technicians to locate and diagnose leaks quickly. This minimizes downtime and reduces repair costs.
4.5 Versatile Applications
Ultrasound leak detection works for a wide range of systems, including gas lines, water pipes, compressed air systems, and industrial machinery.
4.6 Safe for Hazardous Environments
Because it is a non-contact method, ultrasound leak detection can be used in environments where gas leaks or chemical leaks pose safety risks.
4.7 Cost-Effective
By detecting leaks early, ultrasound technology helps prevent costly repairs, water damage, and energy waste. It’s an investment that pays off in long-term savings.
5. Applications of Ultrasound Leak Detection
Ultrasound leak detection is widely used across various industries and applications. Here are some common areas where this technology is invaluable
5.1 Residential Plumbing
- Hidden Pipe Leaks: Detects leaks behind walls, under floors, and within ceilings.
- Water Heater Leaks: Identifies leaks in water heaters or related plumbing connections.
5.2 Commercial Buildings
- HVAC Systems: Finds leaks in air ducts, refrigerant lines, and ventilation systems.
- Compressed Air Systems: Reduces energy waste by identifying leaks in pneumatic tools and lines.
5.3 Industrial Facilities
- Manufacturing Equipment: Detects leaks in hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- Chemical Plants: Locates leaks in pipes carrying hazardous chemicals.
5.4 Automotive Industry
- Brake and Fuel Systems: Identifies leaks that could compromise vehicle performance and safety.
- Air Conditioning Systems: Finds refrigerant leaks to maintain cooling efficiency.
5.5 Utilities and Infrastructure
- Municipal Water Systems: Identifies leaks in underground water mains.
- Gas Lines: Detects leaks in natural gas and propane distribution systems.
6. How to Conduct Ultrasound Leak Detection
While professional technicians are typically equipped to perform ultrasound leak detection, understanding the basic steps can help you appreciate the process
- Preparation: Ensure the system is pressurized. For gas leaks, confirm proper safety procedures.
- Scan the Area: Move the ultrasonic detector’s sensor across the suspected leak area.
- Listen and Observe: Use headphones to hear the converted sounds and watch the visual display for intensity changes.
- Pinpoint the Leak: Identify the exact location by narrowing down the area with the loudest signal.
- Document Findings: Record data on the leak’s location, size, and severity for repair planning.
7. Limitations of Ultrasound Leak Detection
While ultrasound is highly effective, it does have some limitations
- Background Noise: Loud environments can sometimes interfere with detection, though advanced filters can mitigate this issue.
- Requires Pressurized Systems: Leaks need to produce turbulence, which means systems must be under pressure for accurate detection.
- Operator Skill: Successful detection relies on the technician’s experience and ability to interpret signals accurately.
Ultrasound leak detection is a powerful, precise, and non-invasive method for identifying leaks in a wide range of applications. By using high-frequency sound waves, technicians can quickly and accurately pinpoint leaks in water, gas, and industrial systems, saving time, money, and resources.
Understanding how ultrasound is used in leak detection helps you appreciate its value in maintaining efficient, safe, and reliable systems. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, this technology provides a proactive approach to leak management, preventing small issues from turning into costly disasters.